The Fluidic Ignitor is an innovative ignition system developed for in-space propulsion using green propellants such as methane. This unique technology enables reliable and repeatable ignition of rocket engines both on the ground and in space, making it ideal for applications such as satellite attitude control, Orbit Transfer Vehicles, and deep space missions. It operates on the principle of fluid dynamic heating, where gas flows through carefully engineered cavities, leading to intense localised heating. This approach eliminates the need for traditional pyrotechnic or electrical ignition systems, improving safety, reusability, and mission flexibility. Its scalability and adaptability make it suitable for a wide range of propulsion modules, from small thrusters to main engine igniters.
The ignitor features a simple, robust design with no moving parts, requires low power for operation, and is free from electromagnetic interference, making it especially suitable for sensitive spacecraft environments. Its compact and efficient configuration enhances overall system reliability and reduces complexity.
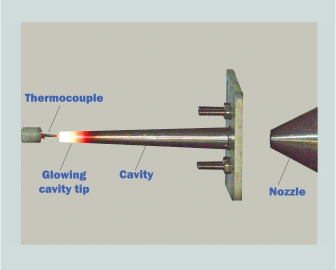
Multiple designs of the fluidic ignitor have been developed and successfully tested at CSIR–NAL. The figure below shows one such design in operation, where the glow at the tip of the ignitor cavity is visible—this hot zone is capable of initiating combustion in a fuel–oxidiser mixture within the rocket engine.